Creating a GitHub Account
Create a personal GitHub account if you don't have one yet.
-
You are advised to choose a sensible GitHub username as you are likely to use it for years to come in professional contexts e.g., in job applications.
-
Strongly recommended: Complete your GitHub profile. In particular,
- Specify your full name.
- Upload a profile photo that matches
our requirements .
Why am I being encouraged to complete my GitHub profile?
The GitHub profile is useful for the tutors and classmates to identify you. If you are reluctant to share your info in your long-term GitHub account, you can remove those details after the module is over or create a separate GitHub account just for the module.
-
You are discouraged from changing your GitHub username during the semester/exam/grading period as it can cause our auto-grading scripts to miss your GitHub activities. If you do change your GitHub username during that period, please let us know immediately.
The purpose of the profile photo is for the reader to identify you. Therefore, choose a recent individual photo showing your face clearly (i.e., not too small) -- somewhat similar to a passport photo. Given below are some examples of good and bad profile photos.
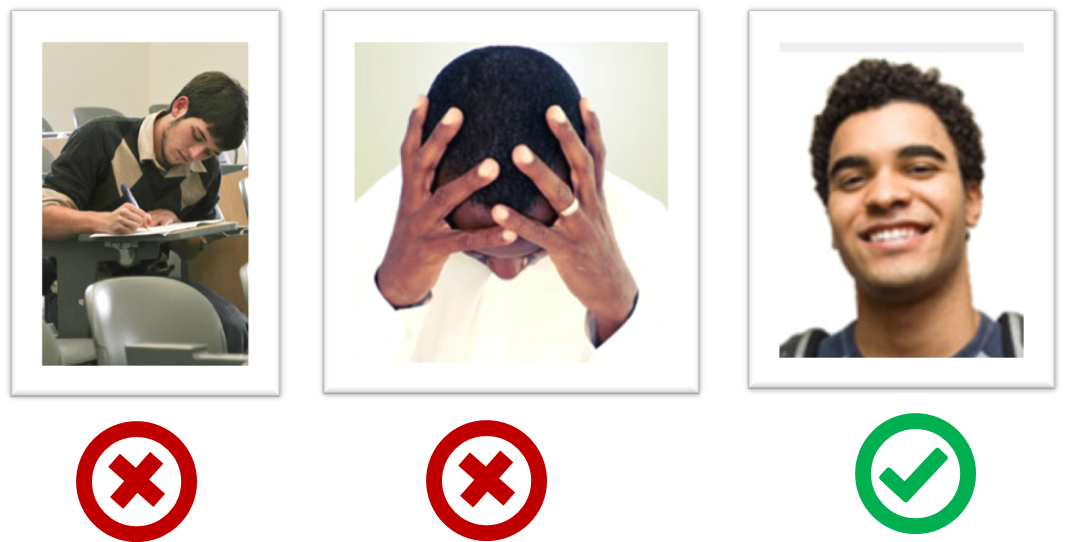

If you are uncomfortable posting your photo due to security reasons, you can post a lower resolution image so that it is hard for someone to misuse that image for fraudulent purposes. If you are concerned about privacy, you may use a placeholder image in place of the photo in module-related documents that are publicly visible.
Guidelines for Reviewing PRs
Follow the Best practices for reviewing PRs @SE-EDU/guides. You are expected to follow all of them.
tP Team Organization Setup
Please follow the organization/repo name format precisely or else our grading scripts will not be able to detect your work.
(/) Only one team member:
After receiving your team ID, one team member should do the following steps:
- Create a GitHub organization with the following details:
- Organization name (all UPPER CASE) :
AY2021S2-TEAM_ID. e.g.AY2021S2-CS2113T-W12-1,AY2021S2-CS2113-T09-2 - Plan: Open Source ($0/month)
- This organization belongs to: My personal account
- Organization name (all UPPER CASE) :
- Add members to the organization:
- Create a team called
developersto your organization. - Add your team members to the developers team.
- Create a team called
tP Team Repo Setup
(/) Only one team member:
The tP project template given to you is a variation of the iP repo you used for the iP, but with some important differences. Please follow instructions carefully, rather than follow what you remember from the iP.
-
Fork the https://github.com/nus-cs2113-AY2021S2/tp repo to your team org.
- This repo (let's call it the team repo) is to be used as the repo for your project.
- Please do not rename the fork Reason: our grading scripts rely on the repo name.
-
Enable the issue tracker.
-
Enable GitHub Actions: Go to the Actions tab and enable workflows by clicking the button. That will enable the GitHub Actions that are already included in the repo you forked.
-
Enable GitHub Pages: Go to the Settings tab and enable
GitHub Pagesfor themaster branch /docs folder(similar to how you did it in the iP).
Remember to choose a theme too by clicking the button (that will create a commit in your repo that is needed in a later step.
After a few minutes, confirm your tP website is available in the correspondinggithub.ioURL. -
Add members. Ensure your team members have the desired level of access to your team repo.
Recommended: Give admin access to 1-2 members and write access to others. -
Create a team PR for us to track your project progress: i.e., create a PR from your team repo
masterbranch to [nus-cs2113-AY2021S2/tp]masterbranch. PR name:[Team ID] Product Namee.g.,[CS2113-T09-2] InsureList. As you merge code to your team repo'smasterbranch, this PR will auto-update to reflect how much your team's product has progressed.
Please fill in these details as specified because they are used by our grading scripts.- PR subject: the name of your product e.g.,
[CS2113-T09-2] InsureList - Description: a 1-2 sentence overview (plain text only, no formatting or links) of your project indicating the target user and the value proposition e.g.,
InsureList helps insurance agents manage detail of their clients. It is optimized for CLI users so that frequent tasks can be done faster by typing in commands.
- PR subject: the name of your product e.g.,
tP Issue Tracker Setup
We recommend you configure the issue tracker of the tP team repo as follows:
- Delete existing labels and add the following labels.
Issue type labels are useful from the beginning of the project. The other labels are needed only when you start implementing the features.
Issue type labels:
type.Epic: A big feature which can be broken down into smaller stories e.g. searchtype.Story: A user storytype.Enhancement: An enhancement to an existing storytype.Task(ortype.Chore) : Something that needs to be done, but not a story, bug, or an epic. e.g. Move testing code into a new folder)type.Bug: A bug
Priority labels:
priority.High: Must dopriority.Medium: Nice to havepriority.Low: Unlikely to do
Bug Severity labels:
severity.VeryLow: A flaw that is purely cosmetic and does not affect usage e.g., a typo/spacing/layout/color/font issues in the docs or the UI that doesn't affect usage.severity.Low: A flaw that is unlikely to affect normal operations of the product. Appears only in very rare situations and causes a minor inconvenience only.severity.Medium: A flaw that causes occasional inconvenience to some users but they can continue to use the product.severity.High: A flaw that affects most users and causes major problems for users. i.e., makes the product almost unusable for most users.
When applying for documentation bugs, replace user with reader.
-
Create following milestones :
v1.0,v2.0,v2.1 -
You may configure other project settings as you wish. e.g. more labels, more milestones
tP Individual Fork Setup
(, , , ...) Every team member:
- Watch the
tprepo (created above) i.e., go to the repo and click on the button to subscribe to activities of the repo. - Fork the
tprepo to your personal GitHub account.
Please do not rename the fork Reason: our grading scripts rely on the repo name. - Clone the fork to your computer.
- Set up the developer environment in your computer by following the the README carefully as the steps are different from the iP.
Do not alter these paths in your project as our grading scripts depend on them.
src/main/javasrc/test/javadocs
tP Workflow
Read
Set Git user.name: We use various tools to analyze your code. For us to be able to identify your commits, we encourage you to set your Git user.name in all computers you use to a sensible string that uniquely identifies you. For example, you can set it to your GitHub username or your full name. If this user name is not set properly or if you use multiple usernames for Git, our grading scripts might miss some of your work.
After installing Git in a computer, you can set the Git username as follows:
- Open a command window that can run Git commands (e.g., Git bash window)
- Run the command
git config --global user.name YOUR_GITHUB_USERNAME(omit the--globalflag to limit the setting to the current repo only)
e.g.,git config --global user.name JohnDoe
More info about setting Git username is here.
Policy on reuse
Reuse is encouraged. However, note that reuse has its own costs (such as the learning curve, additional complexity, usage restrictions, and unknown bugs). Furthermore, you will not be given credit for work done by others. Rather, you will be given credit for reusing work done by others.
- You are allowed to reuse work from your classmates, subject to following conditions:
- The work has been shared publicly by us or the authors.
- You clearly give credit to the original author(s).
- You are allowed to reuse work from external sources, subject to following conditions:
- The work comes from a source of 'good standing' (such as an established open source project). This means you cannot reuse code written by an outside 'friend'.
- You clearly give credit to the original author. Acknowledge use of third party resources clearly e.g. in the welcome message, splash screen (if any) or under the 'about' menu. If you are open about reuse, you are less likely to get into trouble if you unintentionally reused something copyrighted.
- You do not violate the license under which the work has been released. Please do not use 3rd-party images/audio in your software unless they have been specifically released to be used freely. Just because you found it in the Internet does not mean it is free for reuse.
- Always get permission from us before you reuse third-party libraries. Please post your 'request to use 3rd party library' in our forum. That way, the whole class get to see what libraries are being used by others.
Giving credit for reused work
Given below are how to give credit for things you reuse from elsewhere. These requirements are specific to this module i.e., not applicable outside the module (outside the module, you should follow the rules specified by your employer and the license of the reused work)
If you used a third party library:
- iP/tP: Mention in the
READMEfile (under the Acknowledgements section) - tP: Mention in the
Project Portfolio Page if the library has a significant relevance to the features you implemented
If you reused code snippets found on the Internet e.g. from StackOverflow answers or
referred code in another software or
referred project code by current/past student:
- If you read the code to understand the approach and implemented it yourself, mention it as a comment
Example://Solution below adapted from https://stackoverflow.com/a/16252290 {Your implmentation of the reused solution here ...} - If you copy-pasted a non-trivial code block (possibly with minor modifications renaming, layout changes, changes to comments, etc.), also mark the code block as reused code (using
@@authortags-reusedsuffix)
Format://@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused //{Info about the source...} {Reused code (possibly with minor modifications) here ...} //@@authorpersons = getList() //@@author johndoe-reused //Reused from https://stackoverflow.com/a/34646172 with minor modifications Collections.sort(persons, new Comparator<CustomData>() { @Override public int compare(CustomData lhs, CustomData rhs) { return lhs.customInt > rhs.customInt ? -1 : 0; } }); //@@author return persons;
Adding @@author tags indicate authorship
-
Mark your code with a
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}. Note the double@.
The//@@authortag should indicates the beginning of the code you wrote. The code up to the next//@@authortag or the end of the file (whichever comes first) will be considered as was written by that author. Here is a sample code file://@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author sarahkhoo method 3 ... //@@author johndoe method 4 ... -
If you don't know who wrote the code segment below yours, you may put an empty
//@@author(i.e. no GitHub username) to indicate the end of the code segment you wrote. The author of code below yours can add the GitHub username to the empty tag later. Here is a sample code with an emptyauthortag:method 0 ... //@@author johndoe method 1 ... method 2 ... //@@author method 3 ... method 4 ... -
The author tag syntax varies based on file type e.g. for java, css, fxml. Use the corresponding comment syntax for non-Java files.
Here is an example code from an xml/fxml file.<!-- @@author sereneWong --> <textbox> <label>...</label> <input>...</input> </textbox> ... -
Do not put the
//@@authorinside java header comments.
👎/** * Returns true if ... * @@author johndoe */👍
//@@author johndoe /** * Returns true if ... */
What to and what not to annotate
-
Annotate both functional and test code There is no need to annotate documentation files.
-
Annotate only significant size code blocks that can be reviewed on its own e.g., a class, a sequence of methods, a method.
Claiming credit for code blocks smaller than a method is discouraged but allowed. If you do, do it sparingly and only claim meaningful blocks of code such as a block of statements, a loop, or an if-else statement.- If an enhancement required you to do tiny changes in many places, there is no need to annotate all those tiny changes; you can describe those changes in the Project Portfolio page instead.
- If a code block was touched by more than one person, either let the person who wrote most of it (e.g. more than 80%) take credit for the entire block, or leave it as 'unclaimed' (i.e., no author tags).
- Related to the above point, if you claim a code block as your own, more than 80% of the code in that block should have been written by yourself. For example, no more than 20% of it can be code you reused from somewhere.
- GitHub has a blame feature and a history feature that can help you determine who wrote a piece of code.
-
Do not try to boost the quantity of your contribution using unethical means such as duplicating the same code in multiple places. In particular, do not copy-paste test cases to create redundant tests. Even repetitive code blocks within test methods should be extracted out as utility methods to reduce code duplication. Individual members are responsible for making sure code attributed to them are correct. If you notice a team member claiming credit for code that he/she did not write or use other questionable tactics, you can email us (after the final submission) to let us know.
-
If you wrote a significant amount of code that was not used in the final product,
- Create a folder called
{project root}/unused - Move unused files (or copies of files containing unused code) to that folder
- use
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-unusedto mark unused code in those files (note the suffixunused) e.g.
//@@author johndoe-unused method 1 ... method 2 ...Please put a comment in the code to explain why it was not used.
- Create a folder called
-
If you reused code from elsewhere, mark such code as
//@@author {yourGithubUsername}-reused(note the suffixreused) e.g.//@@author johndoe-reused method 1 ... method 2 ... -
You can use empty
@@authortags to mark code as not yours when RepoSense attribute the code to you incorrectly.-
Code generated by the IDE/framework, should not be annotated as your own.
-
Code you modified in minor ways e.g. adding a parameter. These should not be claimed as yours but you can mention these additional contributions in the Project Portfolio page if you want to claim credit for them.
-
At the end of the project each student is required to submit a Project Portfolio Page.
PPP Objectives
- For you to use (e.g. in your resume) as a well-documented data point of your SE experience
- For evaluators to use as a data point for evaluating your project contributions
PPP Sections to include
- Overview: A short overview of your product to provide some context to the reader. The opening 1-2 sentences may be reused by all team members. If your product overview extends beyond 1-2 sentences, the remainder should be written by yourself.
- Summary of Contributions --Suggested items to include:
- Code contributed: Give a link to your code on tP Code Dashboard. The link is available in the Project List Page -- linked to the icon under your profile picture.
- Enhancements implemented: A summary of the enhancements you implemented.
- Contributions to documentation: Which sections did you contribute to the UG?
- Contributions to the DG: Which sections did you contribute to the DG? Which UML diagrams did you add/updated?
- Contributions to
team-based tasks : - Review/mentoring contributions: Links to PRs reviewed, instances of helping team members in other ways
- Contributions beyond the project team:
- Evidence of helping others e.g. responses you posted in our forum, bugs you reported in other team's products,
- Evidence of technical leadership e.g. sharing useful information in the forum
Team-tasks are the tasks that someone in the team has to do.
Examples of team-tasks
Here is a non-exhaustive list of team-tasks:
- Setting up the GitHub team org/repo
- Necessary general code enhancements
- Setting up tools e.g., GitHub, Gradle
- Maintaining the issue tracker
- Release management
- Updating user/developer docs that are not specific to a feature e.g. documenting the target user profile
- Incorporating more useful tools/libraries/frameworks into the product or the project workflow (e.g. automate more aspects of the project workflow using a GitHub plugin)
Keep in mind that evaluators will use the PPP to estimate your project effort. We recommend that you mention things that will earn you a fair score e.g., explain how deep the enhancement is, why it is complete, how hard it was to implement etc..
- OPTIONAL Contributions to the Developer Guide (Extracts): Reproduce the parts in the Developer Guide that you wrote. Alternatively, you can show the various diagrams you contributed.
- OPTIONAL Contributions to the User Guide (Extracts): Reproduce the parts in the User Guide that you wrote.
PPP Format
- File name (i.e., in the repo):
docs/team/githbub_username_in_lower_case.mde.g.,docs/team/goodcoder123.md - Follow the example in the AddressBook-Level3
To convert the UG/DG/PPP into PDF format, go to the generated page in your project's github.io site and use this technique to save as a pdf file. Using other techniques can result in poor quality resolution (will be considered a bug) and unnecessarily large files.
Ensure hyperlinks in the pdf files work. Your UG/DG/PPP will be evaluated using PDF files during the PE. Broken/non-working hyperlinks in the PDF files will be considered as bugs and will count against your project score. Again, use the conversion technique given above to ensure links in the PDF files work.
Try the PDF conversion early. If you do it at the last minute, you may not have time to fix any problems in the generated PDF files (such problems are more common than you think).
PPP Page Limit
| Content | Recommended | Hard Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Overview + Summary of contributions | 0.5-1 | 2 |
| [Optional] Contributions to the User Guide | 1 | |
| [Optional] Contributions to the Developer Guide | 3 |
- The page limits given above are after converting to PDF format. The actual amount of content you require is actually less than what these numbers suggest because the HTML → PDF conversion adds a lot of spacing around content.
Follow the
-
Protect the
masterbranch: You can use GitHub's Protected Branches feature to protect yourmasterbranch against rogue PRs. We suggest the following:- Go the the settings of your team repo.
- Click on the
Branchesoption on the navigation menu on the left. - Click the button. In the Branch protection rule page,
- Specify the Branch name pattern to be
master - Tick the option
Require status checks to pass before mergingto ensure that a branch has to pass CI before it can be merged into themasterbranch - If you think all PRs should be reviewed by someone other than the PR author before they are merged, also tick the
Require pull request reviews before mergingoption.
- Specify the Branch name pattern to be
-
Create issues to represent project tasks so that they can be tracked using the issue tracker features.
-
Create a PR when you implement a project task that updates the code. Remember to use a separate branch for each PR.
You can use GitHub's draft PRs feature to indicate that a PR is not yet ready for merging. -
Get team members to review PRs. A workflow without PR reviews is a risky workflow.
- Follow the Best practices for reviewing PRs @SE-EDU/guides.
PRO TIPLGTMis common abbreviation you can use in the review comments to meanLooks Good To Merge.
- Follow the Best practices for reviewing PRs @SE-EDU/guides.
-
Go breadth-first iterative: As you are expected to follow breadth-first iterative approach, almost all code additions to the
masterbranch should take the product from a working version to a slightly better working version.- Bad Let's add all data classes first reason: this is the depth-first approach
- Bad Let's finish the part of the code that saves and loads data first reason: this is the depth-first approach
- Good Let's add code to support simple todo tasks first (i.e., read, delete, save, load)
-
Do not merge PRs failing Continuous Integration e.g., GitHub ActionsCI. The CI status of a PR is reported at the bottom of the conversation tab of the PR page. Here's an example:
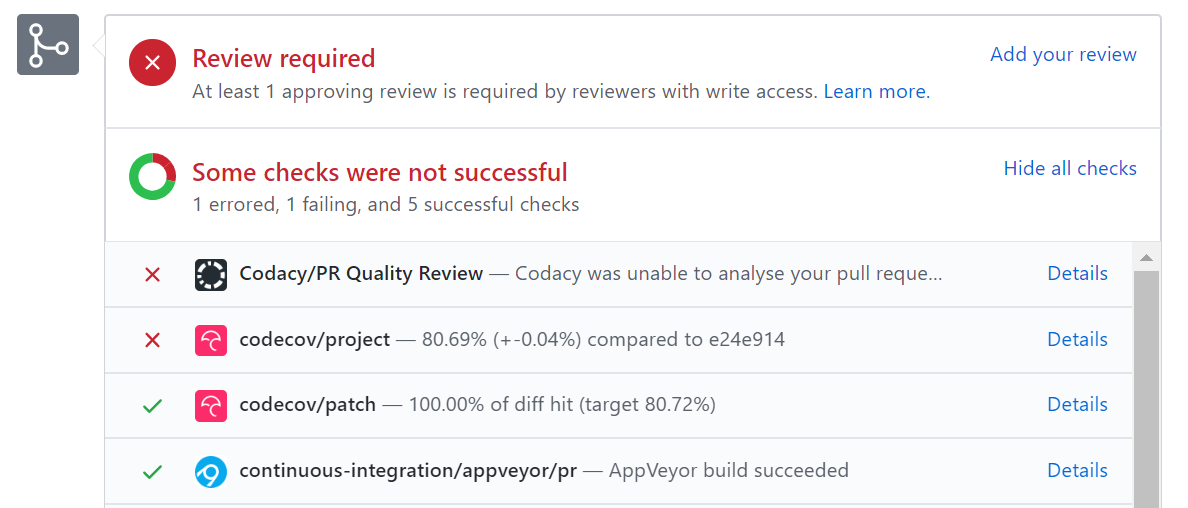
- If there is a failure, you can click on the
Detailslink in corresponding line to find out more about the failure. Once you figure out the cause of the failure, push the a fix to the PR.
- If there is a failure, you can click on the
-
After merging a PR,
- close the corresponding issue.
PRO TIP You can use GitHub'sFixes #123trick to get the issue to close automatically when the PR is merged. - sync your repos with the team rep by pulling the latest
masterfrom the team repo and pushing it to your own fork.
- close the corresponding issue.
-
As you add functionality, update the
input.txtandEXPECTED.txtas well so that the functionality you add gets regression tested automatically every time the code is updated from that point onwards.
Project Management → Revision Control →
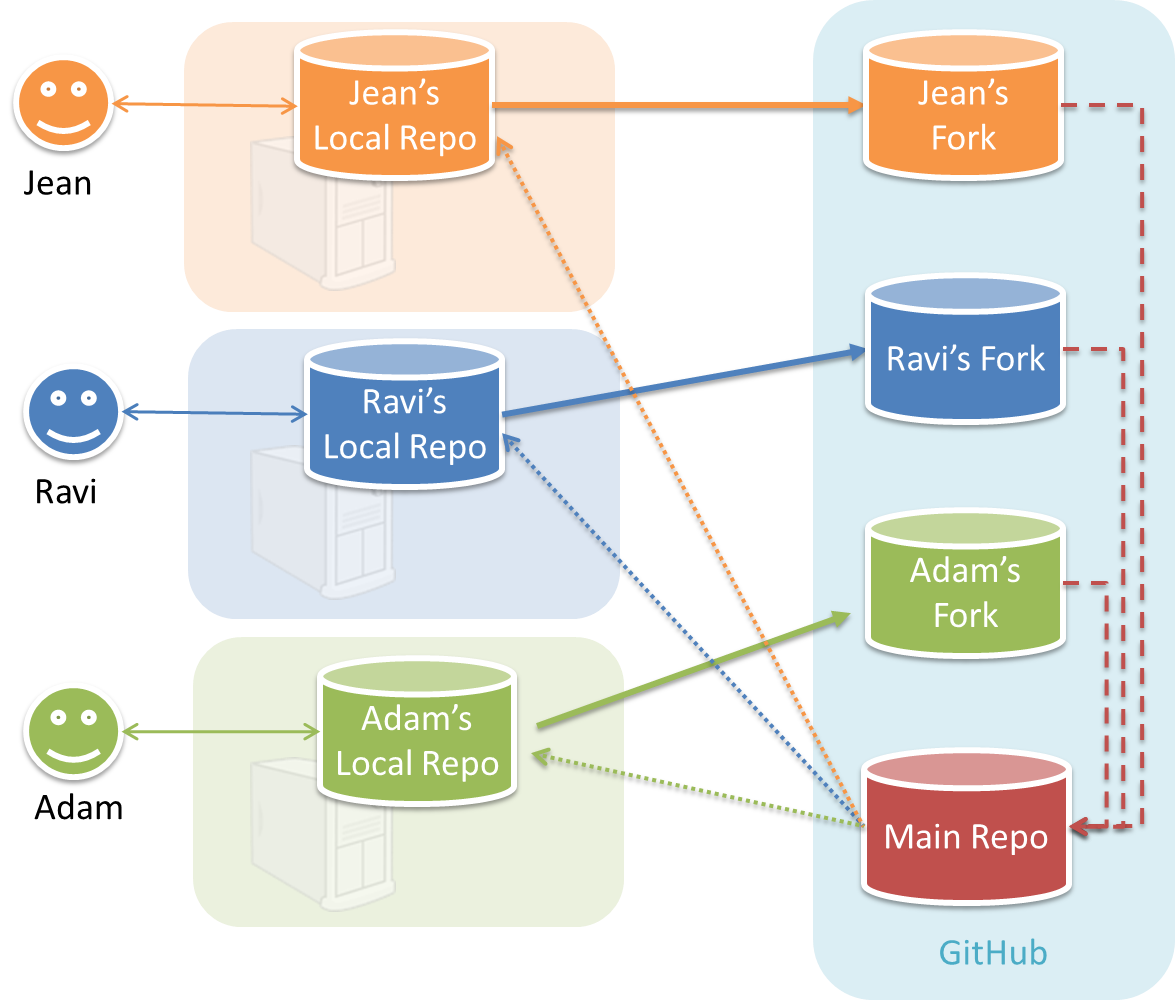
In the forking workflow, the 'official' version of the software is kept in a remote repo designated as the 'main repo'. All team members fork the main repo and create pull requests from their fork to the main repo.
To illustrate how the workflow goes, let’s assume Jean wants to fix a bug in the code. Here are the steps:
- Jean creates a separate branch in her local repo and fixes the bug in that branch.
Common mistake: Doing the proposed changes in themasterbranch -- if Jean does that, she will not be able to have more than one PR open at any time because any changes to themasterbranch will be reflected in all open PRs. - Jean pushes the branch to her fork.
- Jean creates a pull request from that branch in her fork to the main repo.
- Other members review Jean’s pull request.
- If reviewers suggested any changes, Jean updates the PR accordingly.
- When reviewers are satisfied with the PR, one of the members (usually the team lead or a designated 'maintainer' of the main repo) merges the PR, which brings Jean’s code to the main repo.
- Other members, realizing there is new code in the upstream repo, sync their forks with the new upstream repo (i.e. the main repo). This is done by pulling the new code to their own local repo and pushing the updated code to their own fork.
Possible mistake: Creating another 'reverse' PR from the team repo to the team member's fork to sync the member's fork with the merged code. PRs are meant to go from downstream repos to upstream repos, not in the other direction.
Resources
- A detailed explanation of the Forking Workflow - From Atlassian
Revision Control → Forking Workflow
Tools → Git and GitHub →
You can follow the steps in the simulation of a forking workflow given below to learn how to follow such a workflow.
This activity is best done as a team.
Step 1. One member: set up the team org and the team repo.
-
Create a GitHub organization for your team. The org name is up to you. We'll refer to this organization as team org from now on.
-
Add a team called
developersto your team org. -
Add team members to the
developersteam. -
Fork se-edu/samplerepo-workflow-practice to your team org. We'll refer to this as the team repo.
-
Add the forked repo to the
developersteam. Give write access.
Step 2. Each team member: create PRs via own fork.
-
Fork that repo from your team org to your own GitHub account.
-
Create a branch named
add-{your name}-info(e.g.add-johnTan-info) in the local repo. -
Add a file
yourName.mdinto themembersdirectory (e.g.,members/jonhTan.md) containing some info about you into that branch. -
Push that branch to your fork.
-
Create a PR from that branch to the
masterbranch of the team repo.
Step 3. For each PR: review, update, and merge.
-
[A team member (not the PR author)] Review the PR by adding comments (can be just dummy comments).
-
[PR author] Update the PR by pushing more commits to it, to simulate updating the PR based on review comments.
-
[Another team member] Approve and merge the PR using the GitHub interface.
-
[All members] Sync your local repo (and your fork) with upstream repo. In this case, your upstream repo is the repo in your team org.
Step 4. Create conflicting PRs.
-
[One member]: Update README: In the
masterbranch, remove John Doe and Jane Doe from theREADME.md, commit, and push to the main repo. -
[Each team member] Create a PR to add yourself under the
Team Memberssection in theREADME.md. Use a new branch for the PR e.g.,add-johnTan-name.
Step 5. Merge conflicting PRs one at a time. Before merging a PR, you’ll have to resolve conflicts.
-
[Optional] A member can inform the PR author (by posting a comment) that there is a conflict in the PR.
-
[PR author] Resolve the conflict locally:
- Pull the
masterbranch from the repo in your team org. - Merge the pulled
masterbranch to your PR branch. - Resolve the merge conflict that crops up during the merge.
- Push the updated PR branch to your fork.
- Pull the
-
[Another member or the PR author]: Merge the de-conflicted PR: When GitHub does not indicate a conflict anymore, you can go ahead and merge the PR.
After following the given workflow for at least i.e., until the end of v1.0one iteration, optionally, you may adjust the process rigor to suit your team's pace. Here are some examples:
-
Reduce automated tests: Automated tests have benefits, but they can be a pain to write/maintain.
It is OK to get rid of some of the troublesome tests and rely more on manual testing instead. The less automated tests you have, the higher the risk of regressions; but it may be an acceptable trade-off under the circumstances if tests are slowing you down too much.
There is no direct penalty for removing tests. Also noteour expectation on test code . -
Reduce automated checks: You can also reduce the rigor of checkstyle checks to expedite PR processing.
-
Switch to a lighter workflow: While forking workflow is the safest (and is recommended), it is also rather heavy. You may switch to a simpler workflow if the forking workflow if you wish. Refer the textbook to find more about alternative workflows: branching workflow, centralized workflow. Even if you do switch, we still recommend that you use PR reviews, at least for PRs affecting others' features.
-
If you are unsure if a certain adjustment is allowed, you can check with the teaching team first.
- Expectation Write some automated tests so that we can evaluate your ability to write tests.
🤔 How much testings is enough? We expect you to decide. You learned different types of testing and what they try to achieve. Based on that, you should decide how much of each type is required. Similarly, you can decide to what extent you want to automate tests, depending on the benefits and the effort required.
There is no requirement for a minimum coverage level. Note that in a production environment you are often required to have at least 90% of the code covered by tests. In this project, it can be less. The weaker your tests are, the higher the risk of bugs, which will cost marks if not fixed before the final submission.
tP Project Schedule Tracking
In general, use the issue tracker (Milestones, Issues, PRs, Tags, Releases, and Labels) for assigning, scheduling, and tracking all noteworthy project tasks, including user stories. Update the issue tracker regularly to reflect the current status of the project. You can also use GitHub's Projects feature to manage the project, but keep it linked to the issue tracker as much as you can.
Using Issues:
- Record each of the user stories you plan to deliver as an issue in the issue tracker. e.g.,
You can break the user story into issue subject and description in this way:
| title | As a user I can add a deadline |
|---|---|
| Description | ... so that I can keep track of my deadlines |
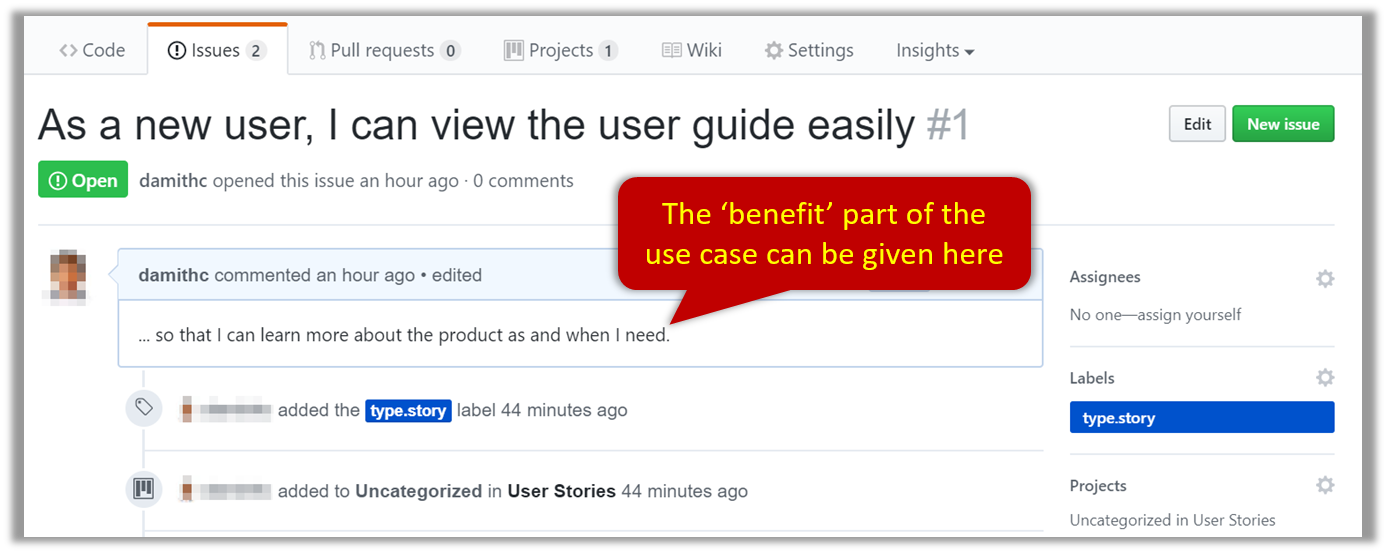
Alternatively, you can put the entire user story in the description.
| title | Add deadline |
|---|---|
| Description | As a user I can so that I can keep track of my deadlines |
In both cases, apply the type.Story label.
-
Assign the
type.*andpriority.*labels to those issues. -
Formalize the project plan by assigning relevant issues to the corresponding milestone.
-
Define project tasks as issues. When you start implementing a user story (or a feature), break it down to smaller tasks if necessary. Define reasonable sized, standalone tasks. Create issues for each of those tasks so that they can be tracked.
-
A typical task should be small enough for one person to do in a few hours. eg.,
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
Write the Developer Guide - Good:
Update class diagram in the Developer Guide for v2.1
- Bad (reasons: not a one-person task, not small enough):
-
There is no need to break things into VERY small tasks. Keep them as big as possible, but they should be no bigger than what you are going to assign a single person to do within a week. eg.,
- Bad:
Implementing parser(reason: too big). - Good:
Implementing parser support for adding of floating tasks
- Bad:
-
Do not track things taken for granted. e.g.,
push code to reposhould not be a task to track. In the example given under the previous point, it is taken for granted that the owner will also (a) test the code and (b) push to the repo when it is ready. Those two need not be tracked as separate tasks. -
Write a descriptive title for the issue. e.g.
Add support for the 'undo' command to the parser- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
prioritycan be omitted if you think they don't help you.
- Omit redundant details. In some cases, the issue title is enough to describe the task. In that case, no need to repeat it in the issue description. There is no need for well-crafted and detailed descriptions for tasks. A minimal description is enough. Similarly, labels such as
-
-
Assign tasks (i.e., issues) to the corresponding team members using the
assigneesfield. Normally, there should be some ongoing tasks and some pending tasks against each team member at any point.
Using Milestones:
Given below are the conditions to satisfy for a milestone to be considered properly managed:
Planning a Milestone (to do within the first week of the iteration):
-
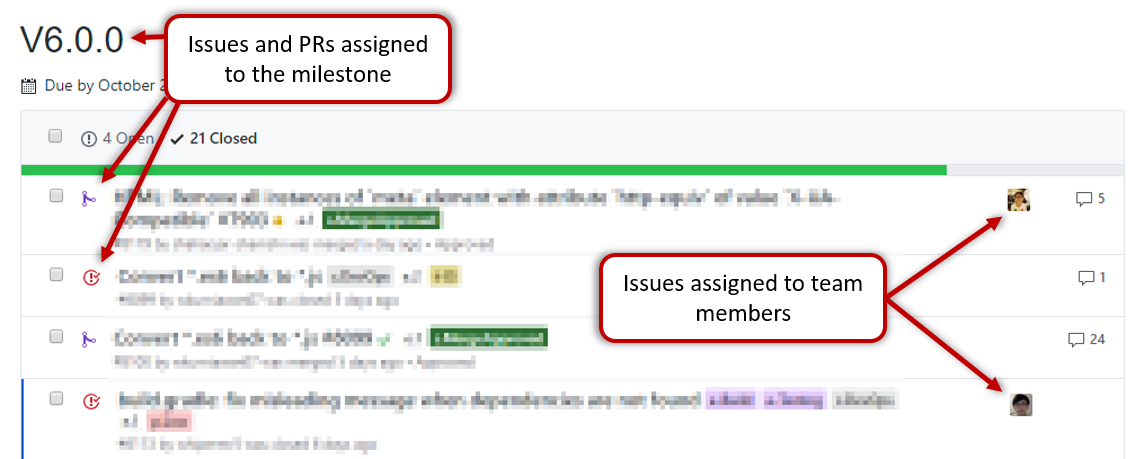
Issues assigned to the milestone, team members assigned to issues: Used GitHub milestones to indicate which issues are to be handled for which milestone by assigning issues to suitable milestones. Ensured issues are assigned to team members. Note that you can change the milestone plan along the way as necessary.
-
Deadline set for the milestones (in the GitHub milestone). Your internal milestones can be set earlier than the deadlines we have set, to give you a buffer.
Wrapping up a Milestone:
-
A working product tagged with the correct tag (e.g.
v2.0) and is pushed to the main repo or a product release done on GitHub (example). -
CI passing for the version tagged/released.
-
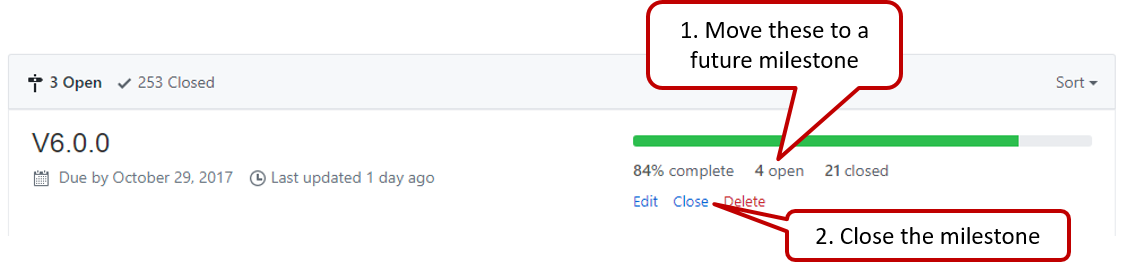
Milestone updated to match the product i.e. all issues completed and PRs merged for the milestone should be assigned to the milestone. Incomplete issues/PRs should be moved to a future milestone.
-
Milestone closed.
Getting started with GitHub Classroom
- Retrieve the links to a particular assignment from the GitHub Classroom exericses page.
Admin GitHub Classroom exercises
List of exercises
Note: As such the exercises are open until end of Week 6. The suggested deadline will help you to keep up with the weekly activities that counts for participation points.
Working on the assignments
Admin Accepting an assignment
Admin Working on the assignment
Working on the assignment
-
Click on the assignment repository, and you will land in the familiar GitHub repository page.
-
Clone the repository to your machine.
-
Open the project as a
gradle projectin IntelliJ
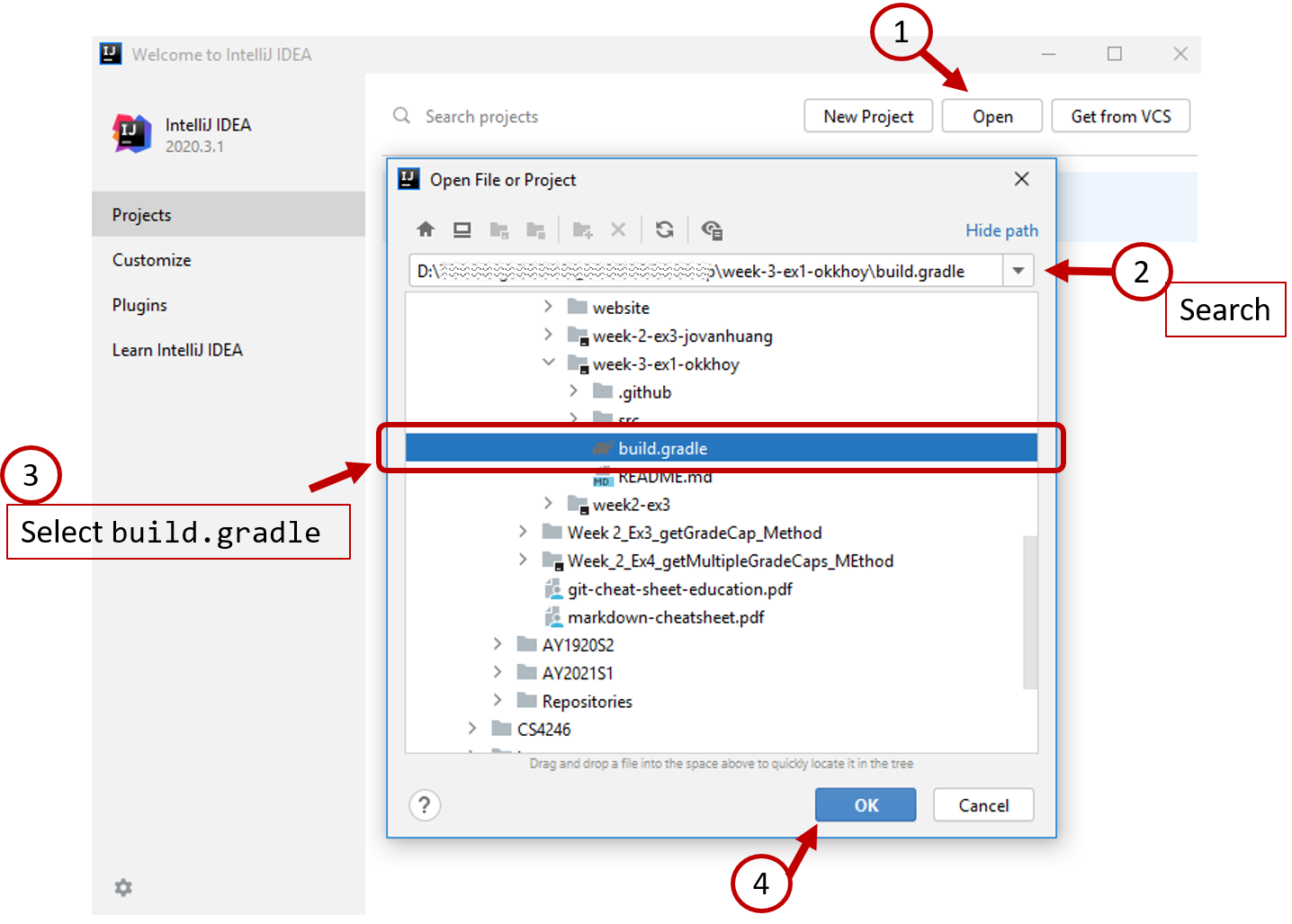
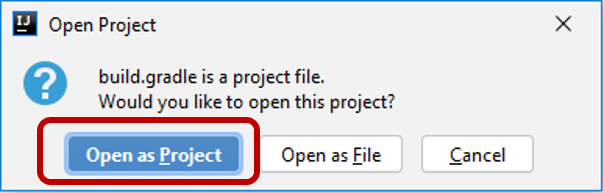
and selectOpen as Project
-
Complete the assignment by adding necessary code/additional files.
-
Test using the given
TestMain.javafile undersrc/test/java
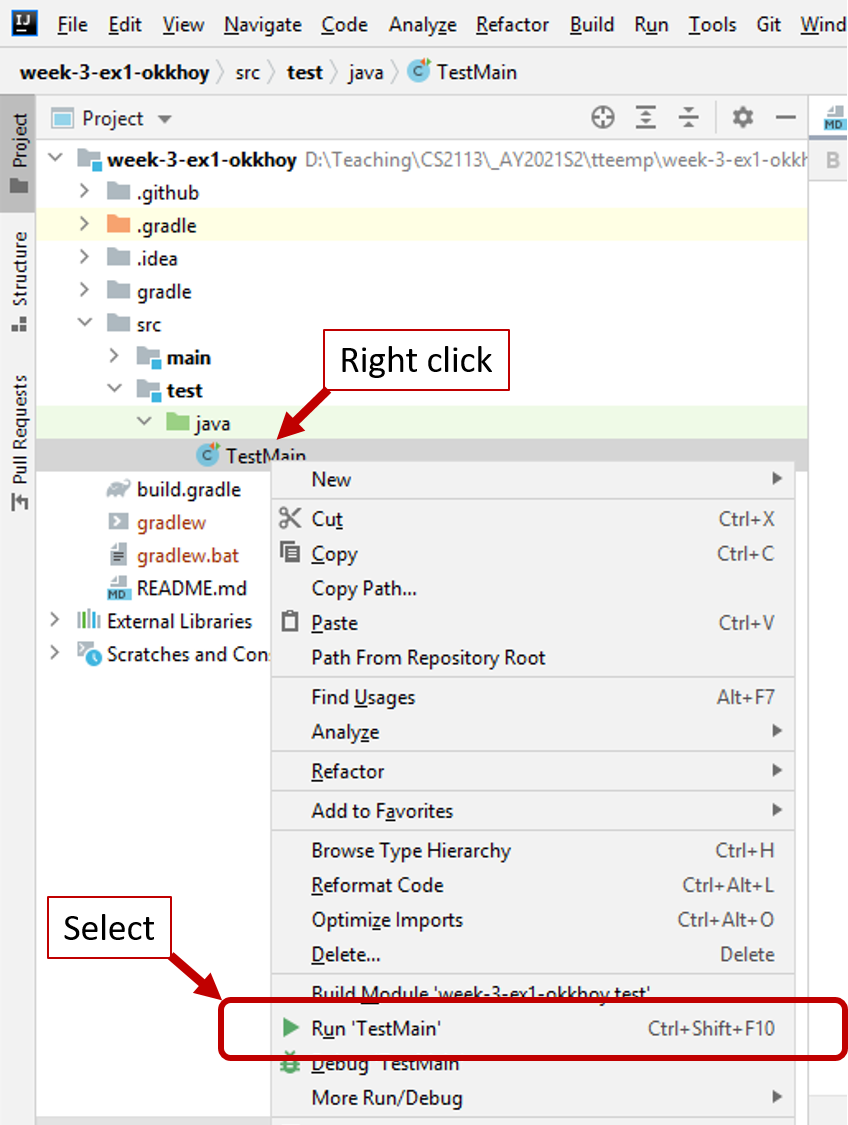
IfRun 'TestMain'doesn't appear for you, open theTestMain.javafile and select Run (from the menubar on top) -> Run
You will be asked to select the configuration. Here select the Gradle configuration (the one with an elephant icon)
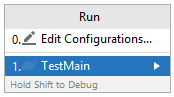
-
Once the tests pass, you can commit and push to your assignment repository. That would be a complete submission.
Registering in GitHub Classroom
- When you start the assignments, for the first time you will be asked to select your identifier to associate your GitHub username to you.
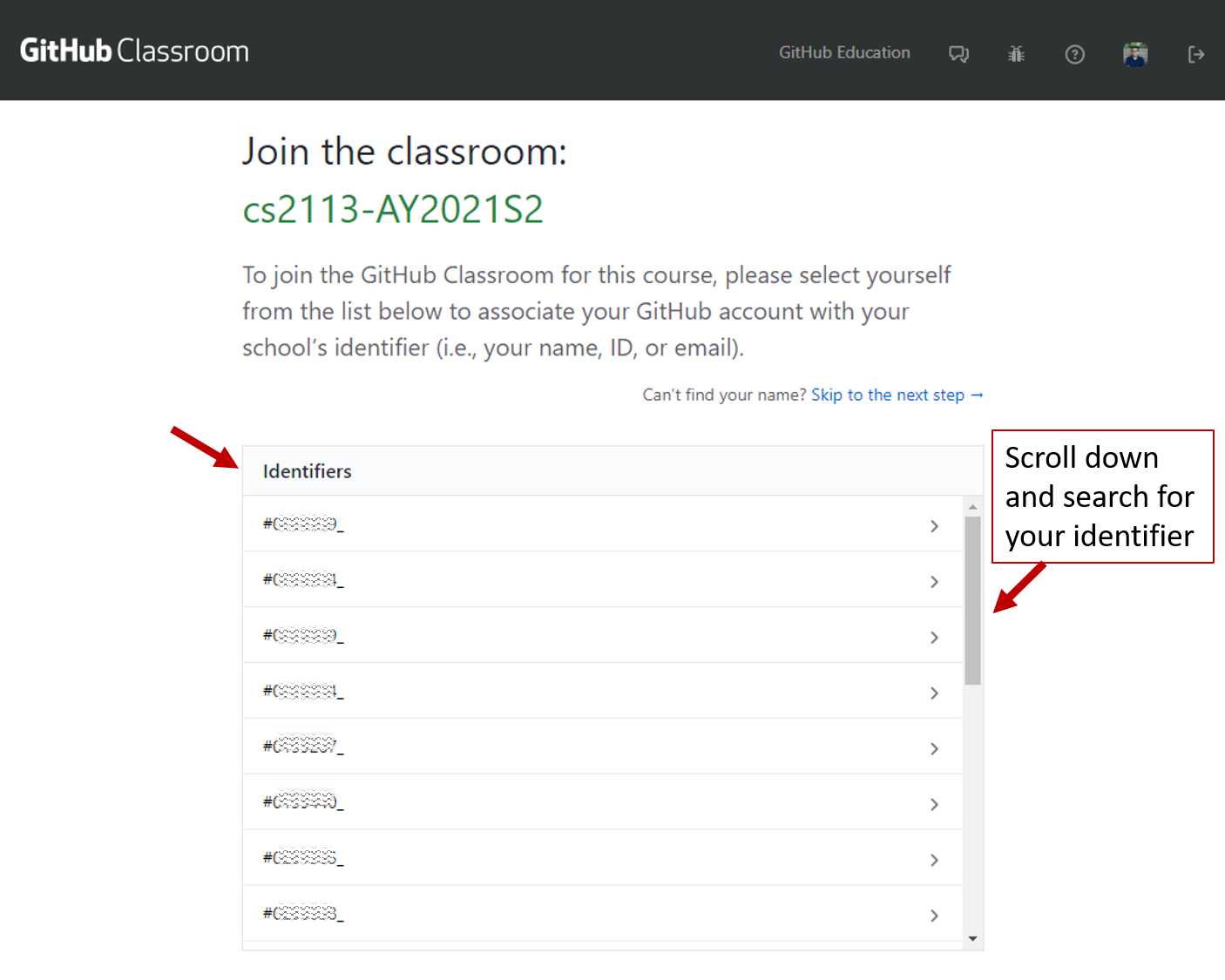
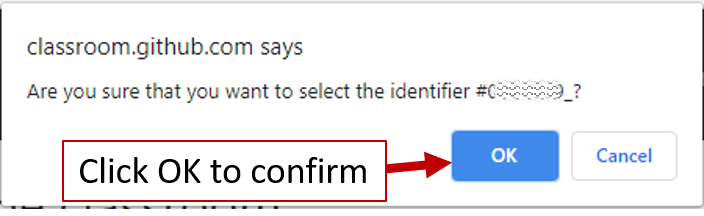
Find your identifier correctly and click on it. GitHub Classroom will ask you to confirm, click OK.
- If you missed this step at the first assignment, GitHub Classroom will ask you to associate your GitHub username to your identifier again when you accept subsequent assignments.
- You need to associate the identifier with your GitHub username only once; once you have linked the two, nothing needs to be done for future assignments.
- Upon linking, we can track your progress, including the past submissions.
Accepting an assignment
-
Upon opening the assignment, you will be presented with a screen to accept it.
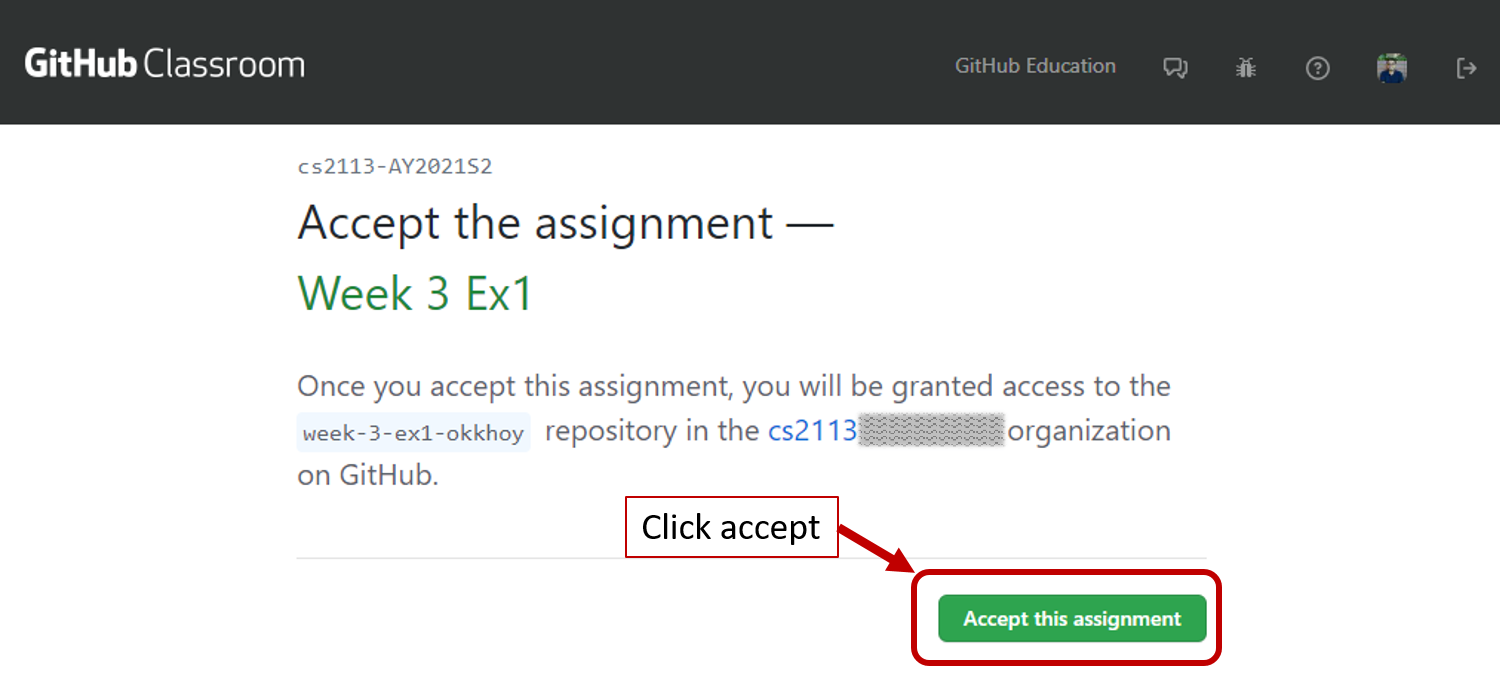
-
Click
Accept this assignment; wait for a moment and refresh the subsequent page. -
Here you will be presented with the link to your assignment repository
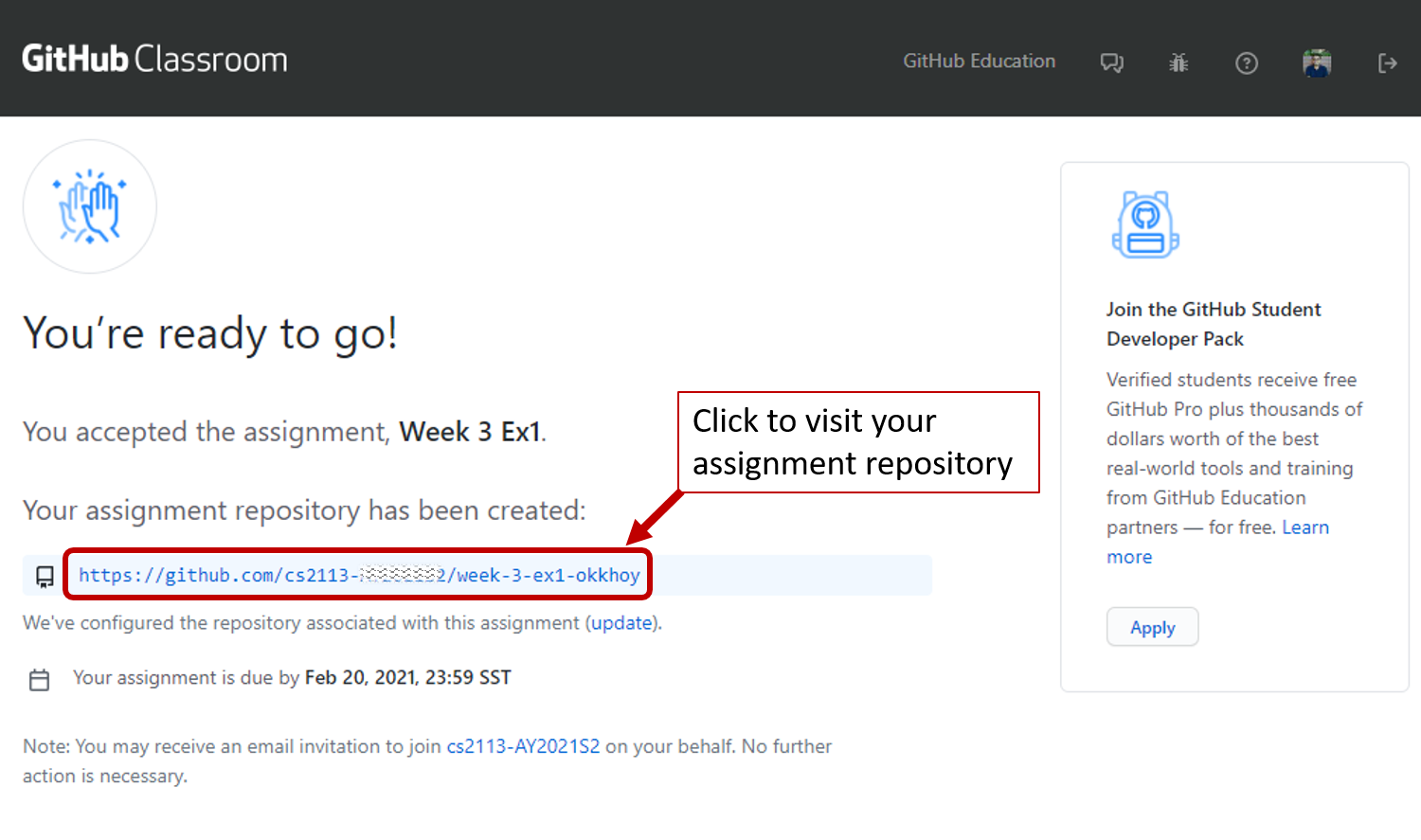
Working on the assignment
-
Click on the assignment repository, and you will land in the familiar GitHub repository page.
-
Clone the repository to your machine.
-
Open the project as a
gradle projectin IntelliJ

and selectOpen as Project

-
Complete the assignment by adding necessary code/additional files.
-
Test using the given
TestMain.javafile undersrc/test/java

IfRun 'TestMain'doesn't appear for you, open theTestMain.javafile and select Run (from the menubar on top) -> Run
You will be asked to select the configuration. Here select the Gradle configuration (the one with an elephant icon)

-
Once the tests pass, you can commit and push to your assignment repository. That would be a complete submission.